In modern telecommunications and networking, fiber optic cables serve as the foundation for high-speed data transmission. These cables use light to carry information over long distances with minimal signal loss, making them essential for internet infrastructure, data centers, and telecommunications networks. However, not all fiber optic cables are the same—different types are designed for specific applications, ensuring optimal performance, durability, and efficiency based on the network’s needs.
Understanding the various fiber optic cable types, including single-mode, multi-mode, armored, and ribbon fiber, helps network engineers, IT professionals, and telecom managers make informed decisions about network design, scalability, and installation environments.
Fiber optic cables are the backbone of modern high-speed data transmission, providing unparalleled speed, bandwidth, and reliability. However, not all fiber optic cables are the same—different types are designed to meet the specific demands of various network environments, distances, and applications. Choosing the right fiber optic cable is essential for ensuring optimal performance, durability, and cost efficiency in a network buildout.
Factors such as signal transmission distance, environmental conditions, and installation requirements play a crucial role in selecting the appropriate cable type. Whether deploying fiber for long-haul telecommunications, data centers, industrial environments, or enterprise networks, understanding the characteristics of single-mode, multi-mode, armored, and ribbon fiber helps network engineers and telecom professionals make informed decisions.
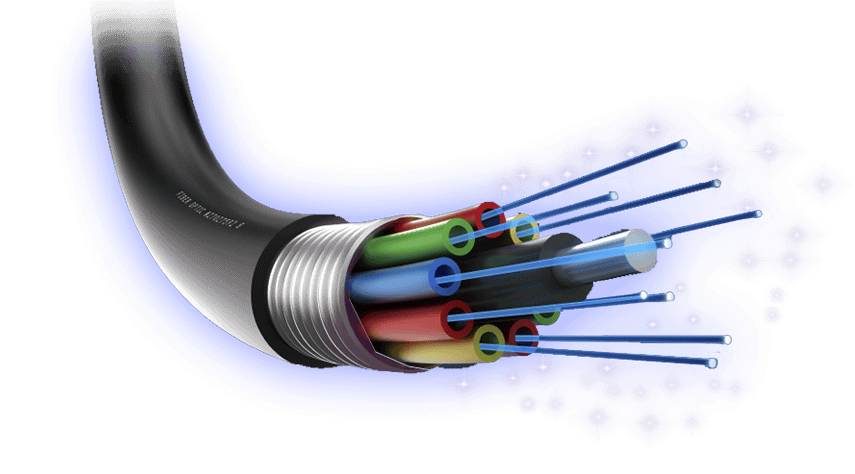
Fiber optic cables are primarily categorized into single-mode and multi-mode fiber, each designed for specific applications based on transmission distance, bandwidth requirements, and network infrastructure. Understanding the differences between these two fiber types is crucial for selecting the right cable for any given deployment.
Single-mode fiber features a small core diameter (typically 8-10 microns) that allows light to travel in a single path, minimizing signal dispersion and attenuation. This makes it the preferred choice for long-distance, high-bandwidth applications.
Key Advantages:
Common Use Cases:
Multi-mode fiber has a larger core diameter (typically 50-62.5 microns), allowing multiple light modes to travel simultaneously. While this increases signal dispersion over long distances, it is cost-effective for short-range, high-speed applications.
Key Advantages:
Common Use Cases:
The decision between single-mode and multi-mode fiber depends on factors such as distance requirements, budget, and network scalability. Single-mode fiber is ideal for long-distance, high-bandwidth applications, while multi-mode fiber is best suited for cost-effective, short-range deployments.
Beyond the standard single-mode and multi-mode fiber, specialized fiber optic cables are designed to meet specific environmental and network requirements. These cables offer enhanced protection, higher density, or improved flexibility for unique deployment scenarios.
Armored fiber optic cables are built with a protective metal or polymer layer surrounding the fiber core, shielding it from physical damage, environmental hazards, and even rodents.
Key Advantages:
Common Use Cases:
Ribbon fiber optic cables contain multiple tightly packed fiber strands in a flat, ribbon-like structure, allowing for high-density deployments. These cables improve efficiency in splicing and are often used in large-scale fiber networks.
Key Advantages:
Common Use Cases:
Both loose tube and tight-buffered fiber optic cables offer flexibility in different environments. The key difference lies in the way the fibers are protected within the cable.
Loose tube cables have buffered fibers housed in water-resistant gel-filled tubes, providing excellent protection in outdoor settings.
Pros:
✔️ Superior water and moisture resistance
✔️ Withstands extreme temperature changes
✔️ Ideal for outdoor and aerial deployments
Cons:
❌ More difficult to terminate
❌ Requires special handling during installation
Common Use Cases:
Tight-buffered cables have an additional protective coating around each fiber, making them more flexible and easier to install indoors.
Pros:
✔️ Easy to terminate and connectorize
✔️ More flexible for routing inside buildings
✔️ No need for gel cleaning during installation
Cons:
❌ Less resistant to water and harsh weather
❌ Not ideal for long-distance outdoor deployments
Common Use Cases:
Each of these specialized fiber optic cables plays a crucial role in building robust, high-performance networks. Choosing the right type depends on installation environment, durability requirements, and network capacity needs.
Fiber optic cables are essential for high-speed, reliable data transmission across various industries. Different fiber types are selected based on performance requirements, environmental conditions, and network demands. Below are key industries that rely on fiber optic technology and how they apply it.
How It’s Used:
Preferred Cable Types:
✔️ Single-Mode Fiber (SMF) – Ideal for long-haul, high-bandwidth telecom networks.
✔️ Ribbon Fiber – Used for dense, high-capacity deployments.
✔️ Armored Fiber – Provides durability for underground or exposed environments.
Data centers depend on high-bandwidth fiber optic cables to ensure seamless data transfer between servers, storage systems, and cloud computing infrastructure.
How It’s Used:
Preferred Cable Types:
✔️ Multi-Mode Fiber (MMF) – Short-range, high-speed connectivity within data centers.
✔️ Tight-Buffered Fiber – Used in rack-to-rack and intra-building connections.
✔️ Ribbon Fiber – Allows for quick mass splicing and high-density cabling.
The military requires ultra-reliable, secure, and rugged fiber optic networks for communication, surveillance, and battlefield operations.
How It’s Used:
Preferred Cable Types:
✔️ Armored Fiber – Protects against environmental hazards and physical damage.
✔️ Loose Tube Fiber – Resistant to water and temperature fluctuations.
✔️ Single-Mode Fiber (SMF) – Ensures long-distance secure data transmission.
Industries such as manufacturing, oil and gas, and transportation rely on fiber optics for automation, monitoring, and operational efficiency.
How It’s Used:
Preferred Cable Types:
✔️ Armored Fiber – Withstands harsh industrial environments and mechanical stress.
✔️ Loose Tube Fiber – Ideal for outdoor and large-scale industrial applications.
✔️ Multi-Mode Fiber (MMF) – Used for short-distance, high-speed industrial connections.
Each industry has unique requirements, but fiber optic technology consistently delivers high-speed, secure, and durable networking solutions for modern infrastructure.
Selecting the right fiber optic cable is crucial for ensuring optimal performance, reliability, and cost efficiency in your network infrastructure. Several factors must be considered, including transmission distance, bandwidth requirements, and environmental conditions. Here’s how to determine the best fiber cable for your project.
The required transmission distance and data speed will largely dictate whether you need Single-Mode Fiber (SMF) or Multi-Mode Fiber (MMF).
Where the fiber will be installed plays a significant role in choosing the appropriate cable type.
If your project requires high-density connections, consider ribbon fiber, which allows for mass fusion splicing, saving time and installation costs.
Ensure that your fiber optic cable meets relevant industry standards for your specific application, whether in telecommunications, government, or industrial sectors.
Choosing the right fiber optic cable is critical to ensuring your network operates at peak efficiency. DataField Technology Services has the expertise to help you select and deploy the best fiber solution for your needs.
