Network modification refers to the process of making strategic changes to existing telecommunications networks to enhance their performance, scalability, and efficiency. These modifications can range from upgrading outdated hardware and software to reconfiguring network architecture or integrating new technologies like 5G and IoT. By adapting to changing demands, network modification ensures that telecom infrastructure remains robust, secure, and capable of supporting modern connectivity requirements.
This page provides a foundational understanding of network modification. For a deeper dive into specific strategies and benefits, visit our Comprehensive Guide to Network Modification.
Imagine a telecom provider experiencing frequent service disruptions during peak hours. By implementing network optimization strategies, such as rerouting data traffic and upgrading key hardware, the provider reduces downtime and improves customer satisfaction. This is just one scenario where network modification proves invaluable.
The telecommunications landscape is constantly evolving, driven by rapid technological advancements and growing user demands. Network modification plays a vital role in keeping pace with these changes by:
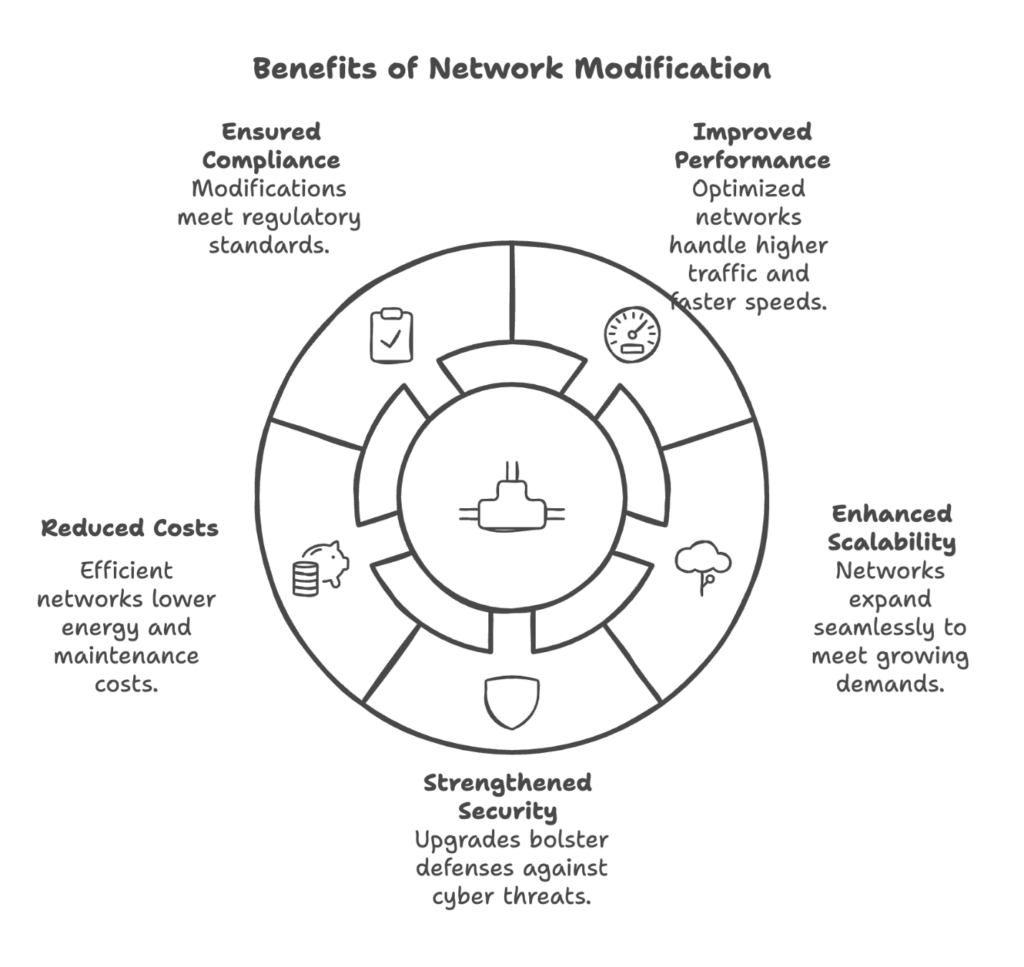
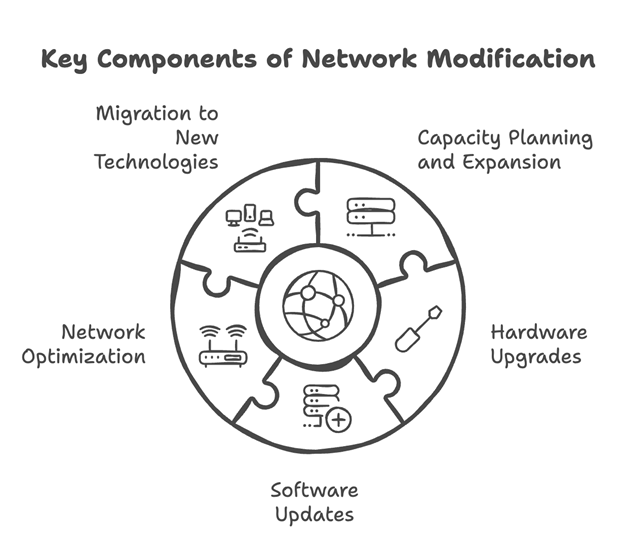
For a detailed exploration of these key areas, check out our Comprehensive Guide to Network Modification.
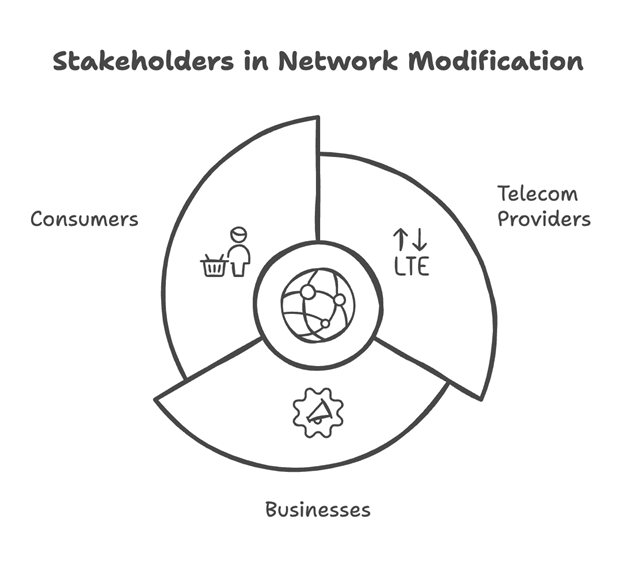
Network modification is beneficial for a wide range of stakeholders, including:
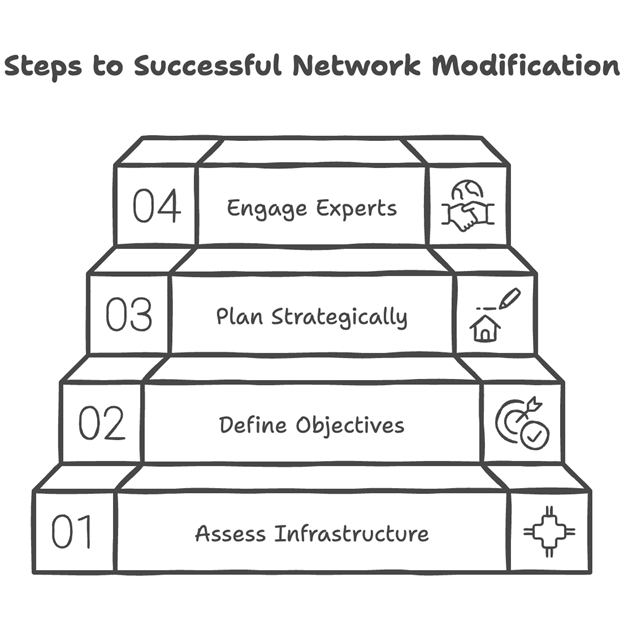
To embark on a network modification project, it is essential to:
This depends on usage patterns and technological advancements. However, most telecom providers review their infrastructure every 2-3 years.
Common indicators include increased downtime, slower speeds, and an inability to support new devices or applications.
Network modification is a transformative process that positions telecom providers and businesses for future growth. By embracing change and investing in strategic upgrades, stakeholders can stay ahead in an increasingly connected world.
The cost of network modification varies depending on the scope of the project, including hardware, software, labor, and downtime considerations. Many organizations conduct a cost-benefit analysis before beginning modifications.
Popular tools include network performance analyzers, traffic monitoring software, and automated configuration tools. These technologies ensure accuracy and efficiency during the modification process.
5G introduces higher bandwidth and lower latency requirements, necessitating upgrades in both hardware and network architecture. Transitioning to 5G often involves substantial reconfigurations and investments.
Network modification is a transformative process that positions telecom providers and businesses for future growth. By embracing change and investing in strategic upgrades, stakeholders can stay ahead in an increasingly connected world.
For in-depth insights and advanced strategies, visit our Comprehensive Guide to Network Modification.